Sustainable development is the concept that human societies must live and meet their needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The formal definition of sustainable development was developed for the first time for the Brundtland Report commissioned by the United Nations in 1987.
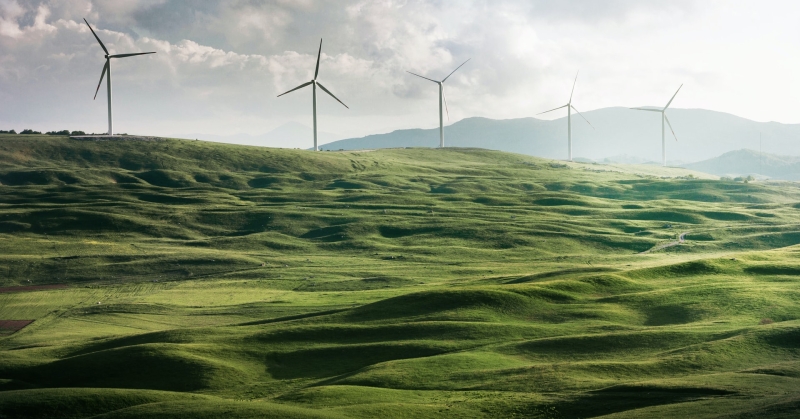

The report stated that critical global environmental problems were primarily the result of the enormous poverty of the South and the non-sustainable patterns of consumption and production in the North
Specifically, sustainable development is a way of organizing society so that it can exist in the long term. This means taking into account both the imperatives present and those of the future, such as the preservation of the environment and natural resources or social and economic equity. So these two conditions: a strong, healthy and just society and living within environmental limits are fundamental in achieving sustainable development.
The idea of environmentally sustainable economic growth is not new. Many cultures over the course of human history have recognized the need for harmony between the environment, society and economy.
How can we achieve sustainable development?
Many of the challenges facing human beings, such as climate change, water scarcity, inequality and hunger, can only be solved from a global perspective and by promoting sustainable development: a commitment to social progress, environmental balance and economic growth.
As a framework to achieve sustainable development, the United Nations approved the 2030 Agenda containing the Sustainable Development Goals, a series of common goals to protect the planet and ensure the well-being of all people. These common goals require the active involvement of people, businesses, governments and countries around the world.
The principles of sustainable development
The principles of sustainable development may be based on different theories and manifestos. They can be summarized as follows:
- The human being at the center: the survival and quality of life of human beings is the focus of sustainable development.
- Principle of equity for the eradication of poverty: implies equitable distribution of resources to meet basic needs (food, clothing and housing) and provide equal opportunities.
- Principle of solidarity with future generations: sustainable development takes into account the commitment to the well-being of future generations.
- Preservation of natural resources and the environment: the preservation of the environment and the resources it provides are a fundamental condition for quality of life and survival.
- Common but differentiated responsibility: we are all jointly responsible for caring for the environment according to the degree to which we affect it.
- State responsibility: States must set limits to environmental overexploitation and discourage indiscriminate consumption.
- International cooperation: States must cooperate with each other by sharing knowledge for the protection of the environment and the achievement of sustainable development. Likewise, the international community should help to ensure the sustainable development of peripheral countries.
Examples of sustainable development
Use of clean or alternative energies. Wind, solar and geothermal energy, among others, are energy sources that have a lower impact on the environment than hydroelectric plants.
Substitution of fossil fuels for biofuels. Fossil fuels generate large CO2 emissions, which have an impact on global warming. In addition, the way they are obtained is very invasive and the recovery time of fossil fuels is so long that they are considered a non-renewable resource and, therefore, could be depleted.
Recycling. Recycling involves the use of materials that have already been manufactured. It is a way of containing and reducing pollution from waste production.
Reduction of intensive agriculture. It involves making appropriate use of agriculture that does not deplete the soil's capacity to provide nutrients.
Reforestation. It is the repopulation of land with plants and trees when they have been intervened to obtain resources.
Reduction of energy consumption. The less energy we consume, the lower the levels of energy production, which means less environmental impact and more economic savings.
Development of sustainable cities and sustainable buildings, such as The Edge building in Amsterdam and the BBVA Bancomer Tower in Mexico City.
As we will see more in depth in the next article, entrepreneurship plays an important role in sustainable development because it contributes to driving economic growth by introducing innovative ideas and solutions while generating employment. Entrepreneurship is also a great way to address social problems by identifying business opportunities that contribute to creating a positive impact in society.